

The Waste to Energy Automation Systems Emerging Market Analysis study delivers current market analysis plus a five year market and technology forecast
Waste obtained, is mostly disposed into water bodies or land without properly treating it, and this is polluting the environment. These problems can be mitigated to a certain extent by the adoption of waste to energy technologies. Waste to energy technologies are eco-friendly and can be used as an alternative to landfilling. In the process of landfill waste decomposition, decomposing the waste will release harmful gases, which will pollute soil and spread diseases in surrounding areas of this landfill.
Waste to energy is a profitable business method to retrieve energy from waste; the co-products obtained such as charcoal, bio-oil, and compost also serves various purposes. An increase in investment towards waste to energy plants is expected to increase the demand for automation systems for waste to energy plants.
The rapid rise in waste disposed from the business and residential sector has led to governments across the world to generate electricity and power from waste. Government initiatives in the form of tax benefits and financial incentives coupled with favorable regulatory scenarios is expected to raise the capacity of waste to energy plants across the globe. However, rise in environmental concerns for waste to energy plants is expected to moderately hinder market growth.
The continuous rise in demand for energy and new trends toward reducing the reliance on fossil fuels is expected to increase the investment in developing countries such as China, Brazil, and India. Rapid urbanization and industrialization rates in the developing countries creates challenges in waste management for government authorities.
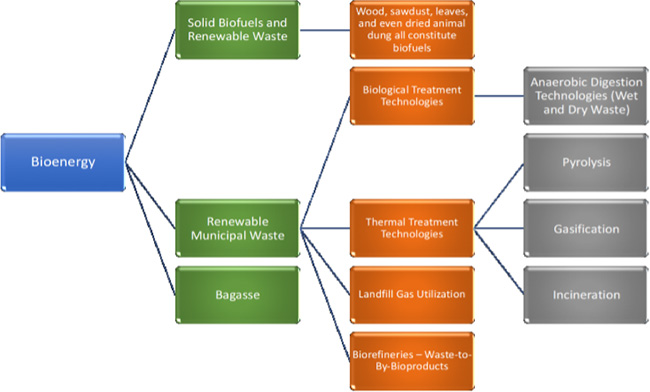
In addition to providing a five-year market forecast, this market research provides detailed quantitative current market data and addresses key strategic issues as follow.
End users should consider designing and building their waste to energy plants in a modular fashion. Modularization breaks down systems, plants, processes, and unit operations into standard, modular components, much like those popular children’s building bricks that can be mixed and matched freely to make any number of different creations.
ARC sees increased interest among process industry end users in applying wireless sensing technology in their installations. Availability of industrial standard protocols (Wireless HART, ISA100) provides a huge catalyst, but some end users still take a “wait and see” attitude in hopes that the wireless field communications standards will ultimately converge.
End users would prefer to concentrate their key personnel and do more expert monitoring at “centers of excellence.” These may be located at major plants or at corporate offices. Often, the information resources available center on data historians rather than automation system software. Automation system suppliers have developed industry- specific solutions for remote operations support in areas. These types of solutions could be attractive to utilities if outfitted with different sets of applications and analytics.
As the middle class continues to grow in developing nations coupled with increased demand for waste to energy plant, it’s becoming essential for automation suppliers to establish a global manufacturing presence and aftermarket footprint to satisfy the needs of the growing customer base in these countries.
This market study may be purchased as a concise, executive-level research report in PDF format.
| MIRA Workbook | PDF File | |
| Worldwide (includes regional data) | No | Yes |
Overview of the competitive landscape for automation systems for the waste to energy system market. Key suppliers are identified with a brief description of each. industry participant.

