

Data centers are locations where servers are used to store and analyze data. With increase in demand for data, the data center industry has seen exponential growth in the past decade due to companies embarking on their digital transformation journeys. Data usage across the globe has skyrocketed due to numerous reasons, of which the global pandemic was the main one. There is a lot of computing power that is required to handle all the data efficiently for various purposes like remote working, streaming services, online retail, virtual collaboration, smart cities, data security, networking, and for new age technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, robotics, digital twin, industrial internet of things and so on.
The industrial world's powerhouses are data centers and they are the lifeline that keep the digitized world moving forward. The need for data and power is growing as technology continues to alter how firms operate. Numerous businesses frequently find that this considerable growth in resources is difficult to manage internally or with the current organizational infrastructure. To keep up with the rising demand, many man-hours and staff are needed. A business can outsource its power requirements by using a data center.
 Data centers are advantageous to businesses in a number of ways. Most specifically, they enable a business to put its customers' needs ahead of technology upkeep. In order to facilitate rapid data flow, data center operators are increasingly replacing the traditional 3-tier network with a 2-tier leaf-spine architecture as they become more conscious of the value it offers to consumers. The two-layer data center network's leaf-spine structure enables faster data transfer across physical network cables. The number of fibers required to serve connectivity on the data center campus will thus significantly grow if leaf-spine architecture is used.
Data centers are advantageous to businesses in a number of ways. Most specifically, they enable a business to put its customers' needs ahead of technology upkeep. In order to facilitate rapid data flow, data center operators are increasingly replacing the traditional 3-tier network with a 2-tier leaf-spine architecture as they become more conscious of the value it offers to consumers. The two-layer data center network's leaf-spine structure enables faster data transfer across physical network cables. The number of fibers required to serve connectivity on the data center campus will thus significantly grow if leaf-spine architecture is used.
The daily operations of businesses are dependent largely on their data centers in today's digital world to store, communicate, and transfer data without latency. As a result, a data center is a crucial asset for the digital economy. To build a data center, businesses must take into account a few factors including energy consumption, performance, and protection that can handle sensitive data. The main industries which majorly use data centers are information technology, telecom, and BFSI.
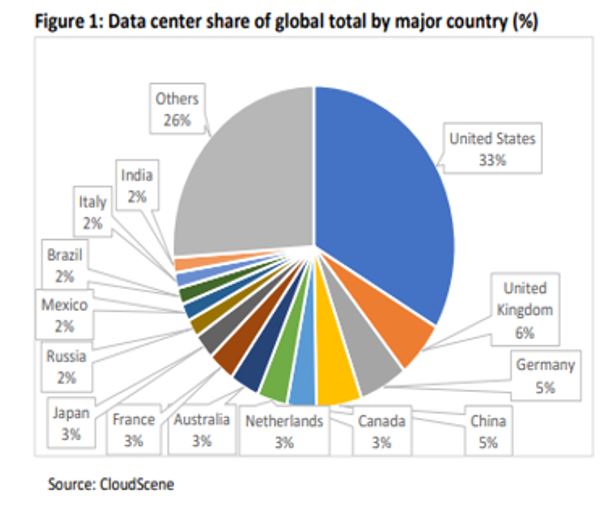
Data center demand varies by country as a result of various market forces and regulations. Higher data center density in particular countries may be a result of industry sector demand. For instance, the UK, one of the biggest financial centers in the world, has the second-largest share of data centers. While Germany is ranked third and has a big manufacturing and industrial capacity with high data demands, the United States and China are ranked first and fourth, respectively.
There are different types of data centers as one size does not fit all. Data center requirements vary based on factors including structure, physical constraints, required densities, and more. The four basic types of data centers are hyperscale, edge, enterprise, and onsite colocation facilities. The scale and how the data center is being used changes for different types of data centers, but the major components always remain the same.
The major components of any data center are classified into IT hardware and supporting hardware for the data center to run without any downtime. The IT hardware mainly consists of storage infrastructure, server infrastructure, and network infrastructure; supporting hardware is the hardware that keeps the data center up and running 24/7, which mainly includes uninterruptible power systems (UPS) and cooling systems; these are the main hardware components that make a data center.
Data center UPS are defined as uninterruptible power systems (UPS) used to provide an auxiliary power supply for a short duration while switching between major power sources in a data center. The increase in power quality problems, as well as the frequent occurrence of power cuts, has led to a surge in demand for UPS. Continuous and clean power is essential, especially for critical applications such as data centers. For further details please check this link- Data Center UPS.
Data center cooling systems are used to maintain optimum temperature and humidity levels in data centers, which prevents overheating and eliminates any potential downtime or failure of advanced IT systems. Data center cooling systems also help in environmental management by regulating the ventilation and heat outflow that is generated from IT equipment. For further details please check this link- Data Center Cooling Systems.
We are going through disruptive times. The technological landscape is constantly changing with innovative solutions for data-driven designs, edge computing, networked systems and new approaches. The systems of today serve as the foundation for our digital future. Data centers are one of the primary backbones affecting the digital economy and creating a better tomorrow for the world.

